2025 IRS Bracket Breakdown for Single Filers
Over the next tax season, understanding the 2025 IRS tax brackets for single filers will be necessary for effectively planning your finances. With changes that could impact your tax liabilities, knowing where you fall within these income ranges can help you optimize your return and maximize potential deductions. This guide will provide you with a clear breakdown of the income thresholds and rates, allowing you to navigate your tax situation with confidence and make informed decisions that positively affect your financial future.
Key Takeaways:
- The 2025 IRS tax brackets for single filers show a progressive tax structure, with rates ranging from 10% to 37% based on income levels.
- The income thresholds at which different tax rates apply have been adjusted to account for inflation, impacting the overall tax liability for single filers.
- In 2025, the top tax bracket starts at $223,000, significantly affecting high-income earners, while lower brackets cater to those with more modest incomes.
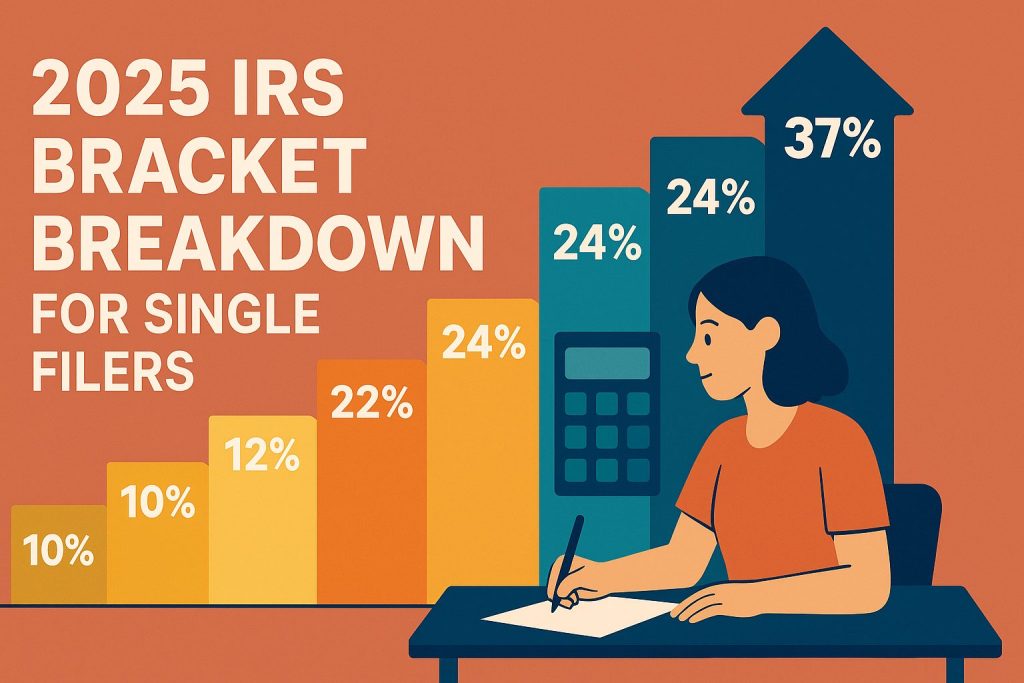
The 2025 Tax Rate Landscape
The 2025 tax landscape for single filers presents a range of rates that can significantly impact your tax liability. With seven income brackets, the rates are structured to progressively tax your earnings, where higher income levels face steeper rates. This makes it vital for you to understand how your income level places you within these brackets and how deductions and credits can affect your overall tax burden.
Key Changes in Tax Rates
For 2025, adjustments reflect a slight increase in the income thresholds for each tax bracket compared to previous years. The 10% rate applies to income up to $11,000, while the 37% rate kicks in for income exceeding $578,125. This broader range means that effective tax rates can be lower for some filers, especially those whose taxable income remains below these limits.
Comparison to Previous Years
When compared to the 2024 tax brackets, significant changes in threshold amounts can affect your tax strategy. For instance, the bottom end of the 12% bracket rose from $11,000 to $12,750, resulting in potential tax savings for many filers. Understanding these shifts allows you to optimize your tax planning for the year ahead.2025 vs. 2024 Tax Brackets
| 2025 Tax Bracket | Threshold |
|---|---|
| 10% | $0 – $11,000 |
| 12% | $11,001 – $45,000 |
| 22% | $45,001 – $160,000 |
| 24% | $160,001 – $207,350 |
| 32% | $207,351 – $500,000 |
| 35% | $500,001 – $578,125 |
| 37% | $578,126+ |
Tracking the changes in tax brackets can provide you with insights into how your tax obligations may evolve. The increase in thresholds, for example, means many individuals may fall into lower tax rates than they would have in the past, reducing their tax liability. It is advisable to revisit your financial strategy, ensuring your deductions and credits align with the new tax landscape to maximize your potential savings.2024 Tax Brackets for Single Filers
| 2024 Tax Bracket | Threshold |
|---|---|
| 10% | $0 – $11,000 |
| 12% | $11,001 – $44,725 |
| 22% | $44,726 – $164,925 |
| 24% | $164,926 – $209,425 |
| 32% | $209,426 – $523,600 |
| 35% | $523,601 – $578,125 |
| 37% | $578,126+ |
Decoding the 2025 Tax Bracket Tiers
Breakdown of Income Ranges
The 2025 tax brackets for single filers feature several key income ranges that determine your tax rate. For example, if your taxable income is up to $11,000, you’ll be taxed at the lowest rate of 10%. As your income increases, you’ll navigate through 12%, 22%, 24%, and up to 37% for the highest earners, which includes incomes above $578,125. Understanding these thresholds allows you to plan your finances more effectively.
Effective Tax Rates vs. Marginal Rates
Your effective tax rate differs significantly from your marginal tax rate. The effective rate reflects the average rate you pay on all your income, while the marginal rate applies only to the highest portion of your income that falls within a specific tax bracket. For instance, if you fall into the 22% bracket, only your income over the previous threshold is taxed at that rate, while the rest is taxed at lower rates. The distinction between effective and marginal rates can significantly impact your tax planning strategy. For example, a single filer earning $50,000 may find their marginal rate is 22%, but their effective rate, taking into account the lower bracket portions of their income, could be closer to 12%. This understanding is key in estimating your overall tax liability and helps you make informed decisions regarding deductions and additional earnings.
Discover more about how bracket creep affects to enhance your knowledge.
The Financial Impact of Bracket Positioning
Your placement in the tax brackets significantly affects your overall financial health. Understanding Federal income tax rates and brackets allows you to strategize your income and deductions effectively. This positioning can influence your take-home pay, retirement contributions, and even investment strategies, making it vital to align your financial decisions with your bracket to reduce your overall tax liability.
Navigating Income Levels for Optimized Taxation
Tax Liability Scenarios for Different Incomes
Evaluating different income levels and their associated tax liabilities clarifies how strategic financial planning can benefit you. For example, earning $40,000 may subject you to a tax rate of 12%, while income just above $90,000 could shift you to a 22% rate. Consequently, it becomes crucial to structure your income through deductions, avoiding an undesirable leap in tax liability.
Let’s explore tax liability with detailed scenarios. A single filer earning $50,000 pays a 12% tax on income up to $44,725, translating to roughly $5,049 in federal tax. Meanwhile, advancing to an income of $100,000 means you incur a 24% tax rate on the portion over $89,075, leading to higher overall taxes despite a greater income gain. Therefore, regular income adjustments and leveraging allowable deductions will help you optimize your taxation, leading to better financial outcomes in the long run.
Discover more about how do us tax to enhance your knowledge.
Deductions and Credits: The Game Changers
Understanding deductions and credits can transform your tax obligations and significantly reduce how much you owe. Deductions lower your taxable income, while credits provide direct reductions of your tax bill. In 2025, single filers can strategically leverage these tools to maximize savings and ensure you retain more of your hard-earned money.
Essential Deductions for Single Filers
Single filers benefit from standard and itemized deductions. For 2025, the standard deduction increases to $14,800. If you itemize, you can consider potential deductions such as mortgage interest, property taxes, medical expenses exceeding 7.5% of your AGI, and charitable contributions, all designed to lower your taxable income significantly.
Tax Credits That Could Minimize Your Bill
Several tax credits can help reduce your bill, including the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the American Opportunity Tax Credit for education expenses. These credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe on a dollar-for-dollar basis, making them exceptionally valuable for your financial strategy.
The EITC can be particularly advantageous for single filers with qualifying income levels, offering credits that can exceed $6,000 depending on your circumstances. Additionally, credits such as the Lifetime Learning Credit can help offset educational costs. Maximizing these credits often depends on accurate documentation of qualifying expenses and income levels, so keeping thorough records is key to benefiting fully from these opportunities.
Strategies to Maximize Your Savings
Implementing effective strategies can enhance your tax savings for the 2025 tax year. By taking advantage of adjustments outlined in the IRS releases tax inflation adjustments for tax year 2025, you can navigate the tax landscape more efficiently. Staying informed about changes in credits, deductions, and income timing allows for optimal planning and potential savings, aligning your financial strategies with the current tax environment.
Income Timing and Tax Planning
Shifting your income to a lower-earning year can significantly affect your tax bracket positioning. For instance, if you anticipate a higher-than-usual income in 2025, consider accelerating deductions or deferring income, such as part of your bonus or year-end commissions, to 2026. This could help keep you in a lower tax bracket and minimize the total taxes owed.
Utilizing Retirement Accounts Effectively
Maximizing contributions to retirement accounts not only prepares you for the future but also provides immediate tax benefits. You can reduce your taxable income by contributing to accounts like a traditional IRA or 401(k), both of which may lower your overall taxable income for the year. In 2025, the contribution limits have increased, giving you an opportunity to save more while enjoying tax breaks.
Fully leveraging retirement accounts involves consistent contributions and careful selection of account types. For 2025, the 401(k) contribution limits are expected to reach $20,500 for individuals under 50 and $27,000 for those 50 and older. You can take advantage of these limits by maximizing your contributions, ensuring that you capitalize on employer matches, and considering a Roth IRA for tax-free growth in retirement. By implementing a strategic approach to these accounts, you not only enhance your long-term financial security but also minimize your taxable income in the present.
Explore our tax brackets guide for 2025 to understand the broader context.
Summing up: 2025 IRS Bracket Breakdown for Single Filers
To wrap up, understanding the 2025 IRS bracket breakdown for single filers is crucial for effective tax planning. By familiarizing yourself with the various income ranges and corresponding rates, you can make informed decisions about your finances. This knowledge will help you maximize deductions and credits, ultimately allowing you to keep more of your earned income. Staying updated with these rates empowers you to navigate tax season with confidence and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
What are the income tax rates for single filers in 2025?
In 2025, the IRS has established the following tax brackets for single filers: – 10% on income up to $11,000 – 12% on income between $11,001 and $44,725 – 22% on income between $44,726 and $95,375 – 24% on income between $95,376 and $182,100 – 32% on income between $182,101 and $231,250 – 35% on income between $231,251 and $578,125 – 37% on income over $578,125 These brackets indicate the percentage at which taxable income is taxed within each range.
How is taxable income determined for single filers in 2025?
Taxable income is calculated by taking your total income and subtracting any deductions and allowances for which you qualify. For single filers, common deductions include the standard deduction, which is projected to be $14,600 in 2025. Additional deductions may apply based on other factors like student loan interest or contributions to retirement accounts. The remaining income after deductions provides the basis for calculating taxes owed according to the applicable tax brackets.
Will tax credits impact the total tax liability for single filers in 2025?
Yes, tax credits can significantly reduce the total tax liability for single filers. Unlike deductions, which lower the taxable income, tax credits reduce the actual amount of tax owed on a dollar-for-dollar basis. For instance, if a single filer has a tax liability of $5,000 and qualifies for a $1,200 tax credit, their final tax due would be $3,800. Common tax credits that may be available include the Earned Income Tax Credit, the Child Tax Credit, and education-related credits.
